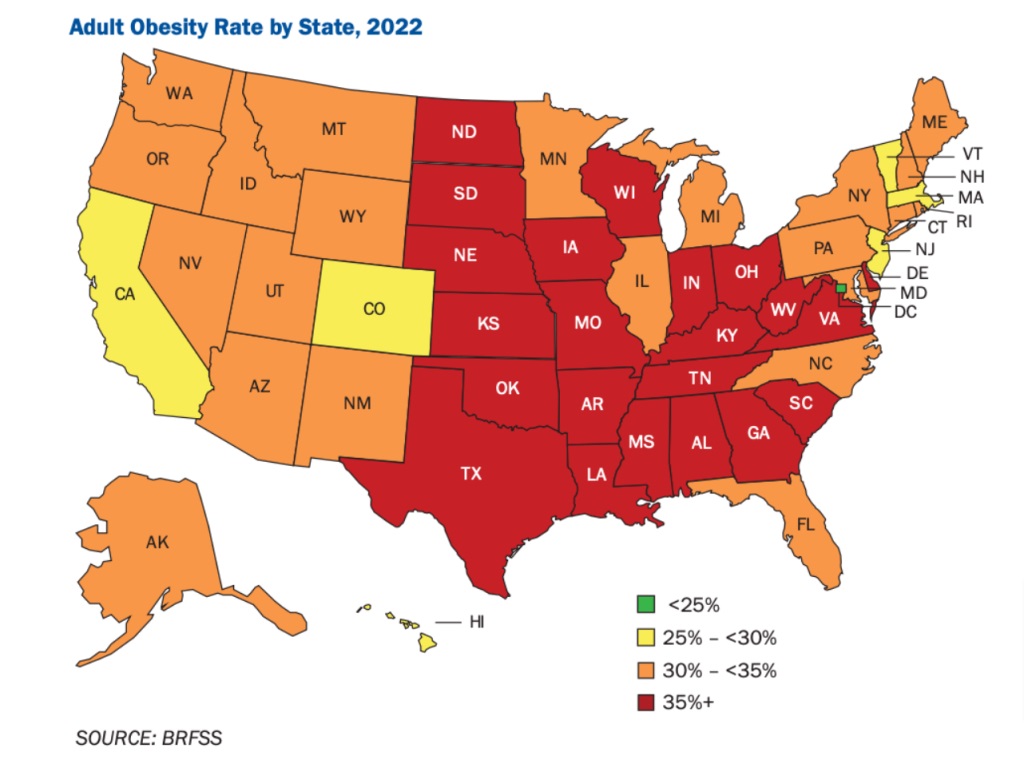
New population data from the CDC in 2023 reveals that over one-third of adults (35%) in 23 states are now living with obesity.
This is a significant change compared to 2013, when no state had an adult obesity prevalence of 35% or higher. Currently, every U.S. state has at least one in five adults (20%) classified as having obesity.
“This data emphasizes the urgent need for better obesity prevention and treatment strategies, starting with the creation of healthier communities.
These communities should provide safe spaces for physical activity, alongside accessible and affordable health care and nutritious food,” stated Karen Hacker, MD, MPH, director of the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
“Preventing obesity early is crucial, as children with obesity are often more likely to become adults with obesity. This underscores why we prioritize state and community investments in child care and family weight management programs.”
The 23 states where adult obesity rates are at or above 35% include: Alabama, Alaska, Arkansas, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, West Virginia, and Wisconsin.
In addition, both Guam and Puerto Rico have obesity rates of 35% or more. These figures are based on self-reported height and weight data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), which tracks adult obesity prevalence by race, ethnicity, and location.
The data also shows that obesity disproportionately affects certain groups. According to BRFSS data collected between 2021 and 2023, notable disparities emerge when obesity rates are broken down by race and ethnicity:
- Among Asian adults, no state (out of 37 states, 1 territory, and DC) has an obesity prevalence of 35% or higher.
- In 16 states, the obesity rate among White adults is 35% or higher (from 47 states, 2 territories, and DC).
- American Indian or Alaska Native adults have obesity rates at or above 35% in 30 states (out of 44 states).
- Hispanic adults have an obesity rate of 35% or higher in 34 states (from 47 states, 3 territories, and DC).
- Black adults have an obesity prevalence of 35% or more in 38 states (out of 46 states, 1 territory, and DC).

“Obesity is a multifaceted disease. There’s a common belief that obesity stems from personal failings such as a lack of willpower to eat healthily or stay active, but this isn’t accurate,” said Ruth Petersen, MD, director of CDC’s Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Obesity.
“A variety of factors contribute to obesity, including genetics, certain medications, inadequate sleep, gut microbiome imbalances, stress, limited access to affordable food, insufficient safe spaces for physical activity, and restricted access to health care.
By understanding these influences, we can develop better strategies for both prevention and treatment.”
The CDC collaborates with communities, states, and tribal groups to enhance health outcomes and reduce obesity rates among populations most at risk of chronic diseases.
Through programs like SPAN, HOP, and REACH, the CDC works to expand access to healthy foods, create safe and accessible areas for physical activity, and promote inclusive obesity prevention and treatment efforts.
These initiatives support 17 states, 50 community and tribal organizations, and 16 land grant universities.
In terms of treatment, obesity management can also involve medications like GLP-1s, which were recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, in combination with lifestyle and behavioral health interventions.
For adults, obesity is defined by having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher. Obesity is associated with numerous health risks, including asthma, heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and severe complications from respiratory illnesses.
Moreover, the stigma surrounding obesity can lead to mental and social health consequences, such as anxiety and negative body image.