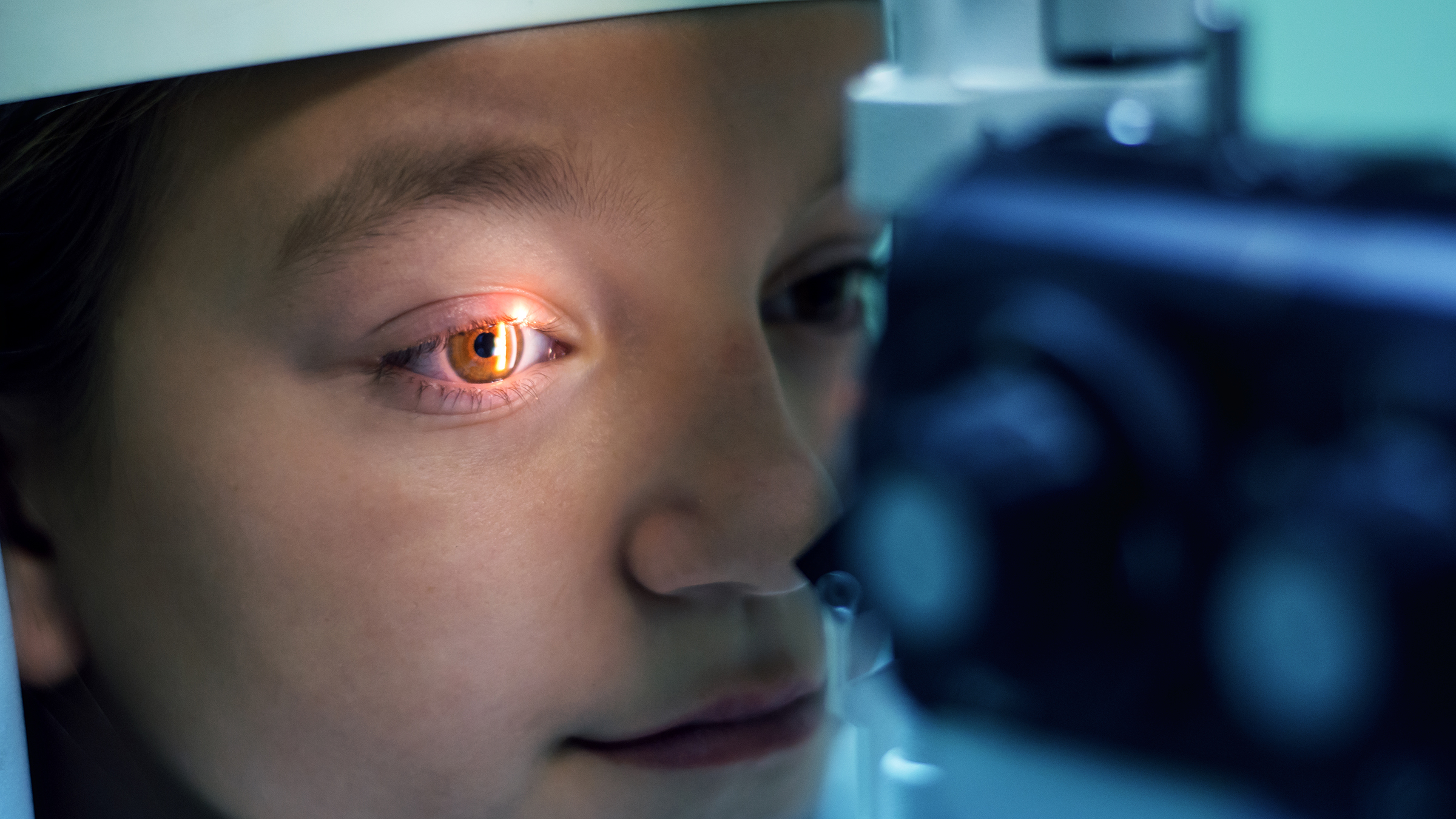
A corneal abrasion is a minor injury that occurs when the cornea, the transparent front part of the eye, gets scratched. This can happen due to contact with various foreign materials such as dust, dirt, sand, or even a piece of paper. The cornea is very sensitive, and even a small scratch can cause significant discomfort.
The symptoms of a corneal abrasion typically include pain, blurry vision, a gritty sensation in the eye, tearing, redness, sensitivity to light (photophobia), and sometimes a headache. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the abrasion. Prompt recognition of these symptoms is important to prevent complications.
Immediate treatment for a corneal abrasion is crucial to avoid infection or further damage. It is recommended to rinse the eye with clean water or saline solution to flush out any foreign objects that might still be present.
Blinking and gently pulling the upper eyelid over the lower one can also help remove small particles. However, it is important to avoid rubbing the eye or using any instruments to remove objects, as this can worsen the injury.
In cases where the abrasion is more severe or does not improve, medical attention should be sought. A healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointment to prevent infection and promote healing. Most corneal abrasions heal within a few days with proper care, but untreated abrasions can lead to more serious issues, such as corneal ulcers.
To prevent further damage or complications, individuals with corneal abrasions should avoid wearing contact lenses until the eye has fully healed. Proper eye protection and avoiding unnecessary eye contact with potentially harmful objects can help reduce the risk of corneal abrasions in the future.