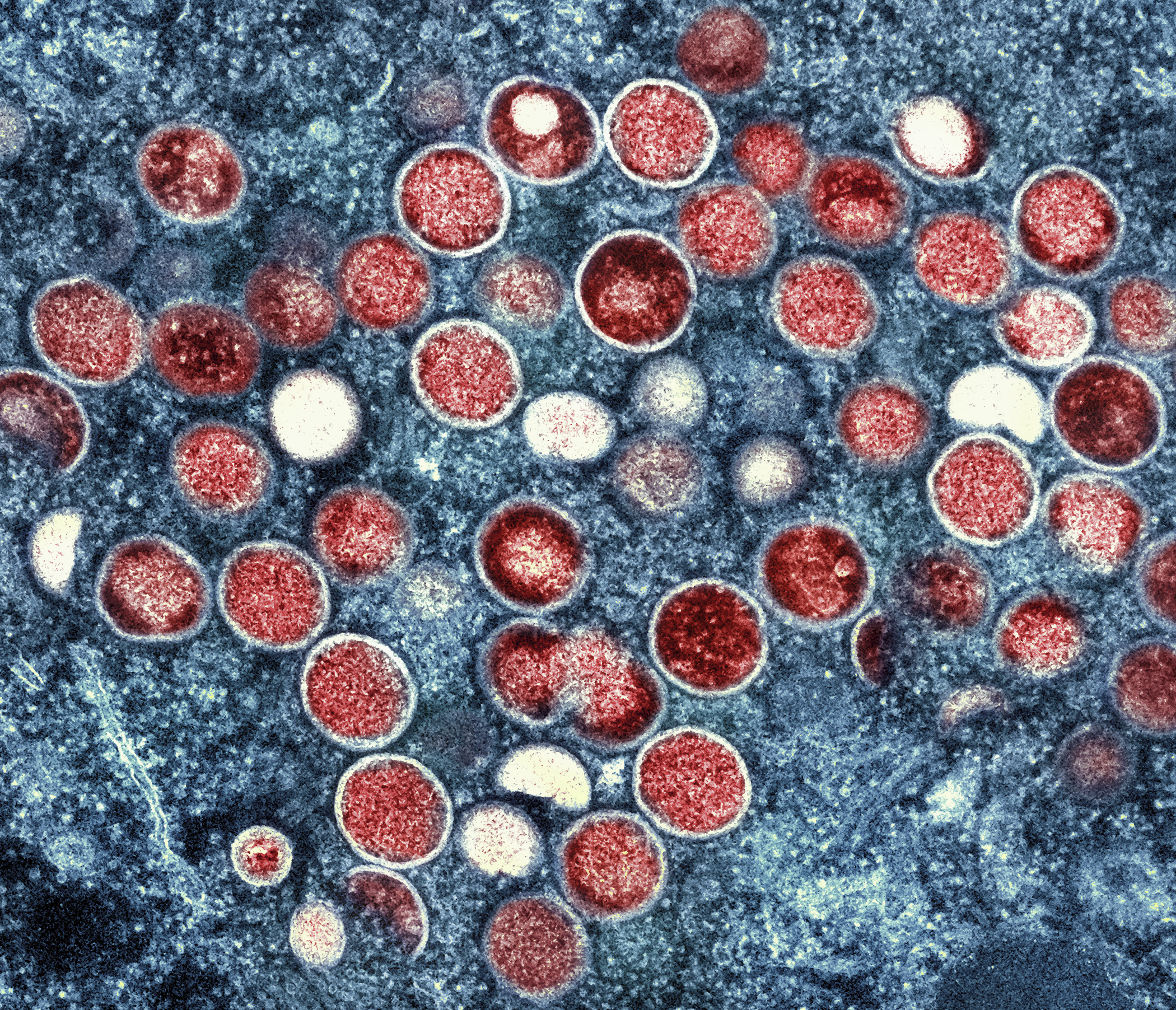
African health officials report a significant 160% spike in mpox (monkeypox) cases this year, with concerns over further spread due to insufficient treatments and vaccines.
The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) revealed that the virus has affected ten African countries, with the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) accounting for over 96% of cases and deaths. Nearly 70% of these cases in Congo are in children under 15, who also represent 85% of the fatalities.
The estimated number of mpox cases this year is around 14,250, almost matching last year’s total, with a 160% increase in cases and a 19% rise in deaths compared to the first seven months of 2023, totaling 456 deaths.
Notably, Burundi and Rwanda reported their first cases this week, while new outbreaks were announced in Kenya and the Central African Republic (CAR), with cases reaching CAR’s densely populated capital, Bangui. In Kenya, a case detected in a traveler from Uganda prompted an outbreak declaration.
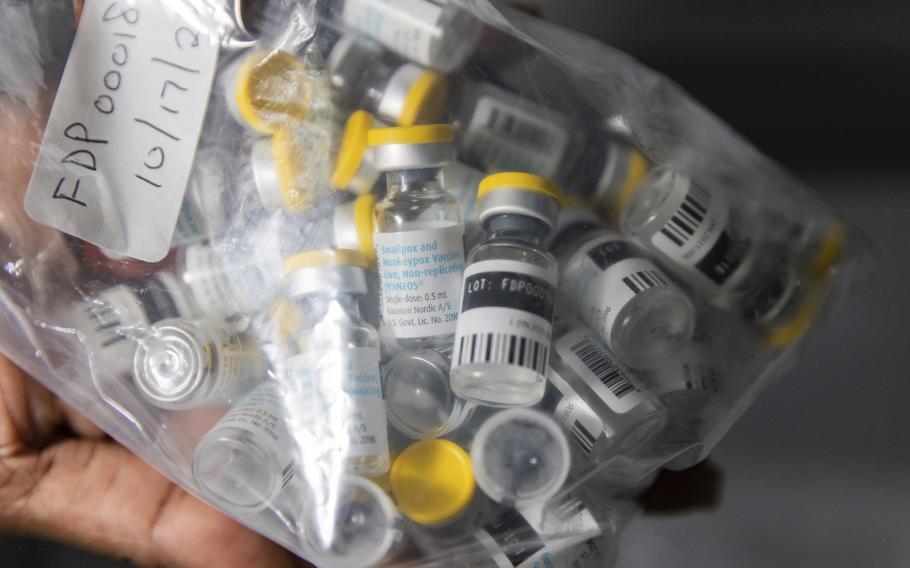
The Africa CDC highlighted that the death rate from mpox in Africa this year, at about 3%, is significantly higher than the global rate during the 2022 mpox emergency, where less than 1% of infected individuals died.
Scientists earlier reported a new, potentially more deadly strain of mpox emerging in a Congolese mining town, capable of causing severe illness and spreading more easily. Recent genetic mutations have been linked to the ongoing transmission among people, with new symptoms and lesions primarily appearing on the genitals, complicating detection.
Doctors Without Borders expressed deep concern over the outbreak’s expansion, especially in camps for displaced persons in Congo’s North Kivu region, emphasizing the risk of rapid spread due to extensive population movements.
Unlike Western countries that have contained outbreaks with vaccines and treatments, African nations, including Congo, face a severe shortage of these resources. This lack of medical support has led health officials to urgently request vaccines to protect the most affected populations.
Despite the ongoing outbreak and potential for international spread, WHO reported in May that no donor funding had been allocated to control mpox in Africa.
However, a recent initiative by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations aims to start a study in Congo and other African countries next month, investigating whether post-exposure vaccination could prevent severe illness and deaths, indicating a critical step towards addressing the outbreak.