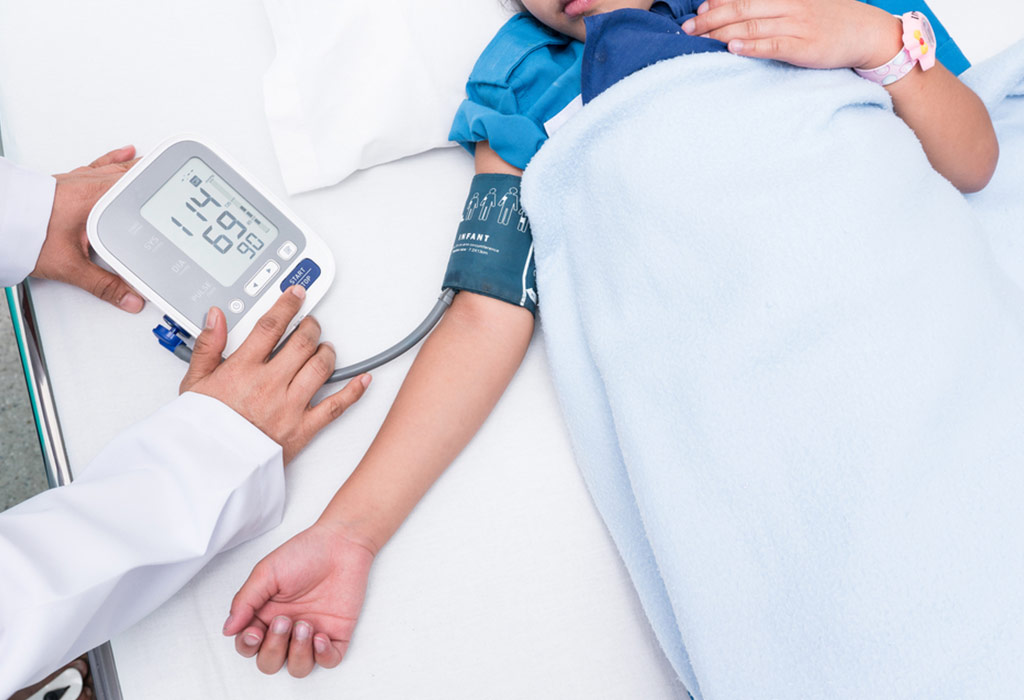
A study conducted by pediatric researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) has revealed that children with hypertension show better medication adherence and improved health outcomes when they receive a 90-day prescription fill compared to a 30-day fill.
The research, published in the journal Pediatric Nephrology, followed 449 pediatric hypertension patients over three years. It assessed the correlation between the prescribed duration of medication supplies and actual dispensation by pharmacies using data from pharmacies and insurance records.
Despite 70% of participants being prescribed 90-day supplies at some point, only 37% managed to obtain these longer-term prescriptions.
The study found no significant difference in the likelihood of receiving a 90-day prescription based on the type of insurance (public or private). However, children with public insurance were less likely to receive the full 90-day supply from pharmacies.
Notably, the children who did receive 90-day fills demonstrated significantly better adherence to their medication regimen (77.5% adherence) compared to those receiving 30-day supplies (58.1% adherence). This better adherence translated into more effective hypertension control as evaluated by healthcare providers.
Dr. Meghan M. McLaughlin, co-author and pediatric nephrology fellow at UR Medicine’s Golisano Children’s Hospital, emphasized the critical role of medication adherence in managing pediatric hypertension.
She pointed out that various factors, such as difficulties accessing pharmacies and affording copays, contribute to inconsistent medication use among patients. By receiving 90-day prescriptions, many of these barriers can be reduced, thus supporting better health outcomes for the children involved.
The importance of adhering to hypertension medication is underscored by the fact that approximately 10% of teenagers with obesity have hypertension, which predisposes them to severe adult health issues, including heart attacks and strokes.
McLaughlin highlighted that increasing the availability of 90-day prescriptions can significantly enhance medication adherence and subsequently improve long-term health prospects for children and teens with hypertension.
Despite the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and Medicare recommending 90-day fills for chronic medications, Medicaid patients often face difficulties accessing these prescriptions.
Although physicians frequently prescribe 90-day fills, pharmacies tend to dispense only 30-day supplies, particularly for children covered by Medicaid. McLaughlin called for nationwide advocacy to align Medicaid policies with CDC and Medicare guidelines.
She also pointed out a positive development with the launch of NYRx, a centralized Medicaid pharmacy program in New York State in April 2023, which aims to enhance access to 90-day fills for children on Medicaid.