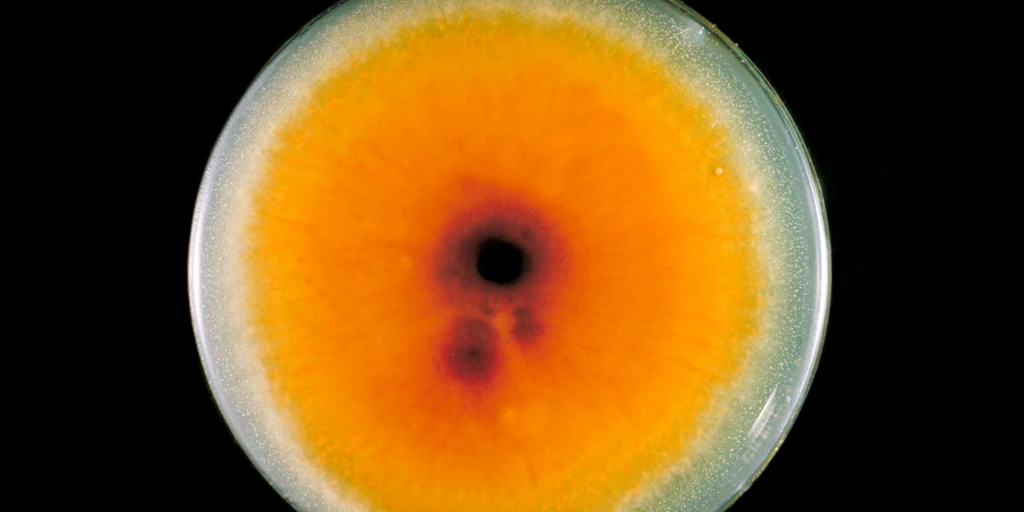
The first case of a highly contagious and rare sexually transmitted fungal infection has been identified in the United States.
The infection, known as Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII (TMVII), is a form of ringworm that is non-fatal but challenging to treat. The case was reported by the medical journal JAMA Dermatology on Wednesday, June 5.
A man in his 30s from New York City developed the infection on his limbs, buttocks, and genitals after traveling to England, Greece, and California, according to the journal.
The man reported having sexual encounters with multiple partners during his travels, though none of his partners showed similar skin symptoms.
Following his diagnosis, the man required over four months to fully recover with the assistance of antifungal medications, NBC News reported.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) noted that 13 cases of Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII were reported in France in 2023.
Of these cases, twelve were associated with men who had sexual contact with other men, according to the organization.
While the fungal infection is not fatal, it can lead to permanent scarring, as noted by JAMA Dermatology.
Trichophyton mentagrophytes type VII can present similarly to eczema, often forming in a circular pattern, according to a press release from NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Due to its resemblance to eczema, it may be overlooked and go untreated for extended periods.
The rashes associated with this infection can easily spread to areas such as the face and limbs (ringworm), the groin (jock itch), and the feet (athlete’s foot), NYU Langone reported.
Dr. Avrom Caplan, an assistant professor of dermatology at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, stated that while it is important for the public to be aware of such infections, there is currently no evidence to suggest that they are widespread.